
[ad_1]
The Schleswig-Holstein consumer advice center warns of a new phishing scam on its internet portal this week. As part of this attack, fraudsters pose as Google and warn the company’s customers in an email about an alleged virus.
Subject doesn’t seem very serious
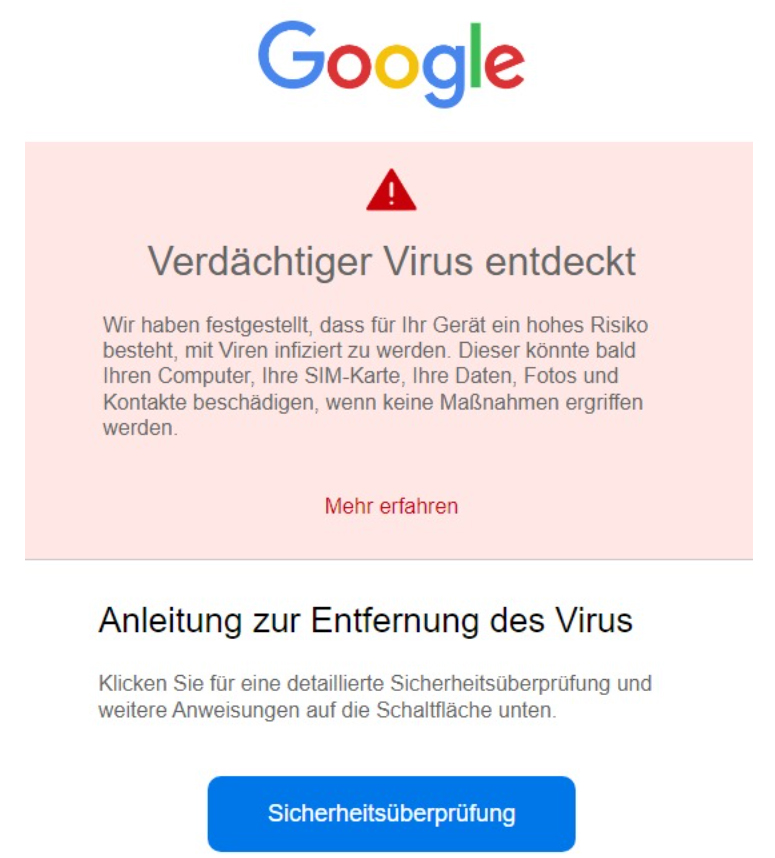
However, the cyber criminals are not really convincing. The subject itself speaks against the seriousness of digital mail: “Important security notification: Your device is in danger! ———— <<<
Alleged virus threat is intended to scare people
In contrast to the subject line, the content and presentation of the email make a “real” impression at first glance. The Google logo, which is located at the top of the email text, is followed by a warning highlighted in red. This is intended to make the recipient believe that their device is at high risk of being infected with viruses. If the email recipient does not take action, the malware can damage data, photos, contacts or even the SIM card, the email continues. Below this is a link that says “Find out more” which the user should click on.
“Security check” promises protection against viruses
If you start to get scared after reading the warning, the phishing email promises a solution with alleged “instructions for removing the virus”. The email asks the recipient to click the large blue “Security Check” button for further instructions and to complete a detailed security check.
consumer center.sh
Fraudsters are after personal data and passwords
Do not click on the “Learn More” link or the “Security Check” button, instead move the phishing email to your spam folder or delete it. Such links usually lead to fake input masks where cyber criminals want to access your personal data and passwords.
When sending phishing emails, you should always observe the following security rules:
- Do not open attachments as they could install harmful malware.
- Do not click on links, especially if the email asks you to do so.
- Do not respond to suspicious emails.
- Do not give out a phone number or other personal contact information
- Take a closer look at the sender’s email address and the web address contained in the email to identify any inconsistencies.
- If you use your work email account, contact the IT team directly.
- Use two-factor authentication in your email program.
- Use antivirus and antispam tools to protect yourself from phishing and malware.
Recognizing phishing emails – tips for limiting damage
[ad_2]
Source link



